The ideal gas law is the final and most useful expression of the gas laws because it ties the. K is a constant.
Boyle S Law Overview Formula Expii
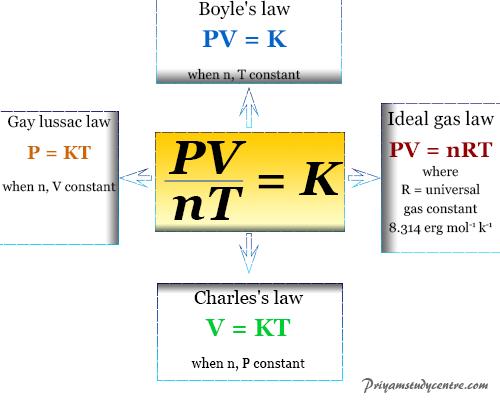
3 Ideal Gas Law Ideal Gas Law PV nRT The pressure of a gas times its volume equals the number of moles of the gas times a constant R times the temperature of the gas.
. In the International System of Units SI the unit of measurement of. P V n R T where R stands for ideal gas constant and equals 83144598 Jmol K. In Newtonian mechanics linear momentum translational momentum or simply momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object.
It is a vector quantity possessing a magnitude and a direction. R is the ideal gas constant. R universal gas constant 83145 Jmol K N number of molecules k Boltzmann constant 138066 x 10-23 JK 8617385 x 10-5 eVK k RN A.
But there is also a. In short the ideal gas law states that the product of one gram molecules pressure and volume is equal to the product of the gass absolute temperature and the universal gas constant. These specific relationships stem from Charless Law Boyles Law and Gay-Lussacs Law.
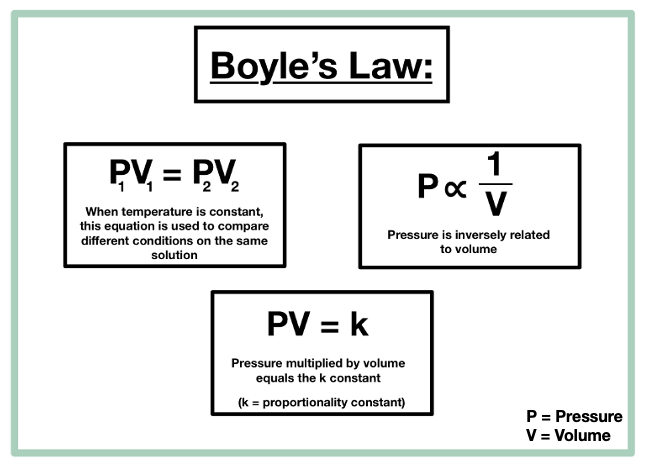
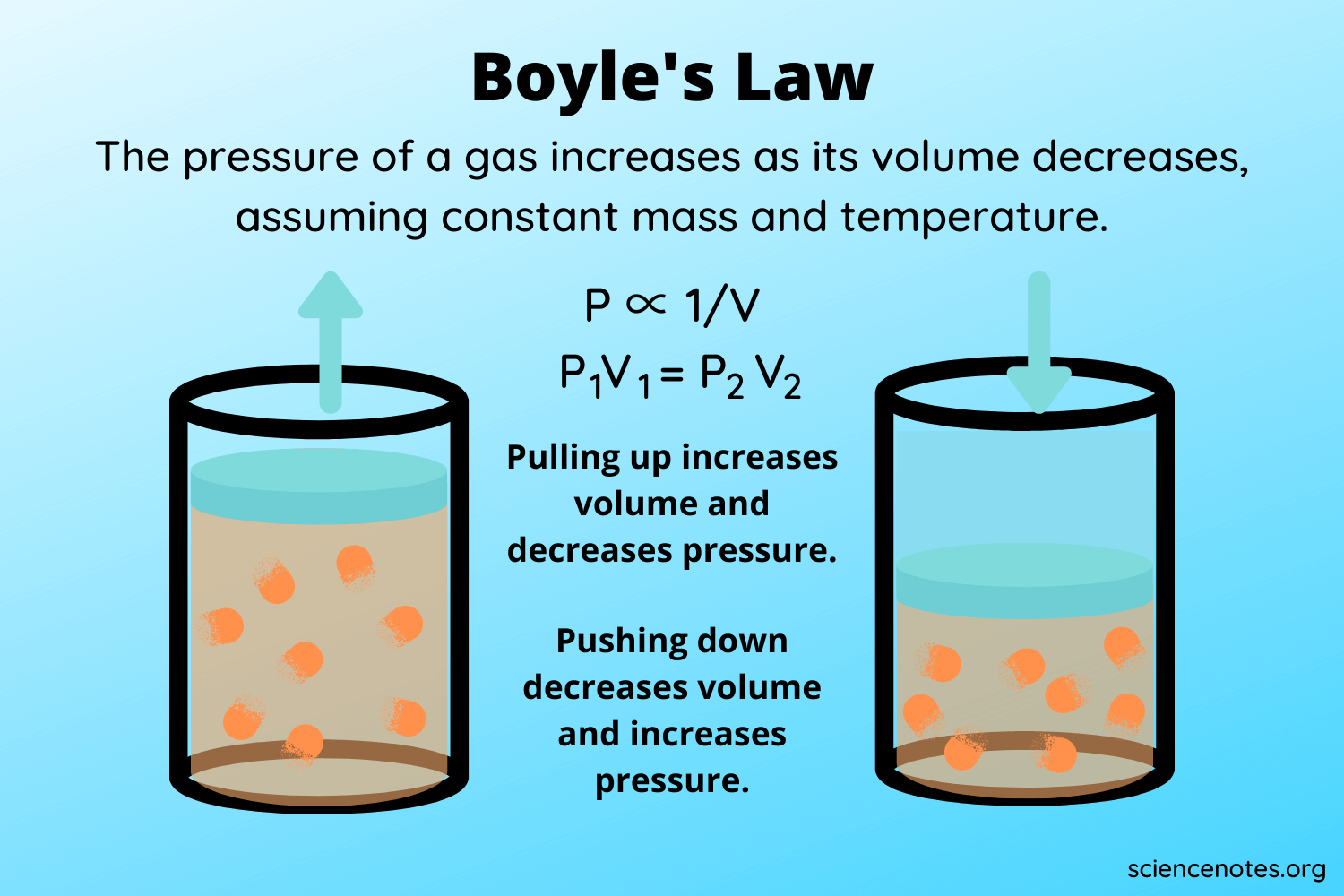
Boyles Law states that the product of the volume and pressure for an ideal gas remains constant. R 8314 462 618 153 24 m. Hence for a given temperature and pressure the molar volume is the same for all ideal gases and is based on the gas constant.
P T. It implies that. The relationship between the pressure and absolute temperature of a given mass of gas at constant volume can be illustrated graphically as follows.
During any process at least two of these properties change which can be compiled in combined gas law formula. According to Boyles law for an ideal gas the pressure of the given mass is inversely proportional to its volume when the temperature is constant. P is the pressure exerted by the gas.
The Ideal Gas Law is a simple equation demonstrating the relationship between temperature pressure and volume for gases. PV k Here k is a constant P is the pressure and V is the volume. The ideal gas equation can be rearranged to give an expression for the molar volume of an ideal gas.
Entropy a brief discussion on entropy change and its effect on the spontaneity of a Process spontaneity of a reaction the expression for entropy change and more with Byjus. PVnRT in which Ppressure VVolume nmoles of substance Rgas constant and TTemperature. T is the absolute temperature of the gas.
Charless Law identifies the direct proportionality between volume and temperature at constant pressure Boyles Law identifies the inverse. Boyles Law Gay-Lussacs Law Combined Gas Laws Grahams Law Ideal Gas Law. Where P is the pressure.
Ideal Gas Law PV nRT 2. Ideal Gas Equation Units. N A Avogadros number 60221 x 10 23 mol The ideal gas law can be viewed as arising from the kinetic pressure of gas molecules colliding with the walls of a container in accordance with Newtons laws.
N is the amount of substance. An ideal gas can be described by several parameters which are pressure p volume V temperature T and the amount of particles nThey are correlated with the equation. If m is an objects mass and v is its velocity also a vector quantity then the objects momentum p is.
The ideal gas law describes the property of a hypothetical ideal gas. The mathematical expression of Gay-Lussacs law can be written as follows. V is the volume.

Boyle S Law Practice Problems Youtube
0 Comments